What is Basic Software (BSW)?
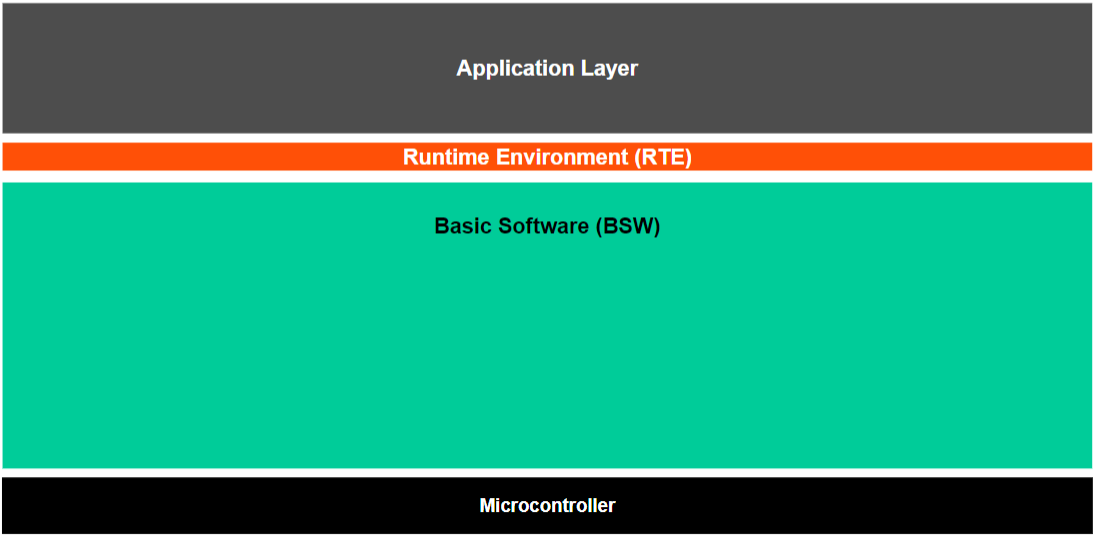
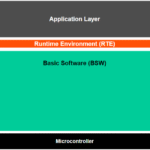
Basic Software is the foundation layer in the AUTOSAR Classic Platform. It includes standardized software modules that provide core functionality and services for higher layers, such as the Runtime Environment (RTE) and Application Software Components.
Think of BSW as the “operating system + middleware + drivers” for automotive ECUs.
BSW Architecture Overview
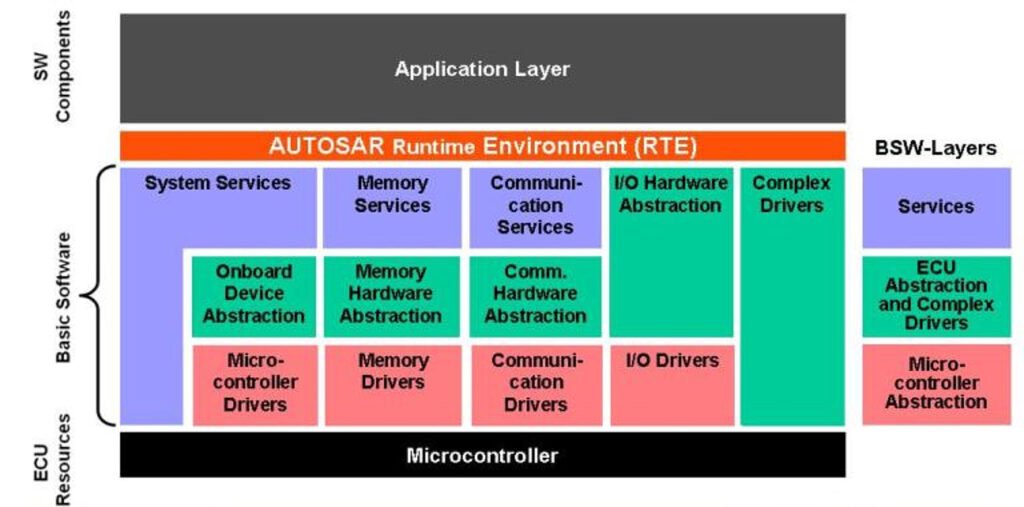
BSW is divided into four major stacks:
1. Microcontroller Abstraction Layer (MCAL)
- Lowest layer of BSW
- Provides a hardware abstraction of microcontroller peripherals (e.g., ADC, PWM, CAN, SPI)
- Allows higher layers to be hardware-independent
✅ Example: The CAN driver in MCAL converts AUTOSAR standard API calls into hardware-specific instructions.
2. ECU Abstraction Layer
- Abstracts the hardware details outside the microcontroller, such as sensors, actuators, and communication chips
- Enables reuse of higher layers across different ECUs
✅ Example: If you switch to a new sensor model, only this layer needs to change, not the application.
3. Service Layer
- Provides system-wide services, such as:
- Diagnostic communication (DoIP, UDS)
- Memory management (NvRAM)
- Watchdog and ECU state manager
- Operating System (OS)
✅ Example: The Watchdog Manager ensures the ECU resets safely if the software hangs.
4. Complex Device Drivers (CDD)
Used for non-standard hardware or when performance-critical requirements prevent using the standard MCAL path
- CDDs interact directly with hardware and are managed manually
Note: CDDs should be used cautiously, as they bypass standardization.
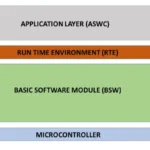
How BSW Interacts with Other AUTOSAR Layers
- The Application Layer contains user-defined components like speed control, lighting control, etc.
- The RTE (Runtime Environment) connects Application Components with BSW services.
- BSW offers essential services under the hood, such as:
- Communication over CAN/LIN/FlexRay
- Diagnostic handling
- Scheduling tasks
- Accessing memory and sensors
Benefits of Using BSW
✅ Standardization – promotes interoperability between ECUs from different vendors
✅ Reusability – BSW modules can be reused across different vehicle platforms
✅ Scalability – supports various hardware and software configurations
✅ Abstraction – allows development teams to focus on application logic instead of hardware specifics
✅ Quality and Safety – BSW modules are often safety-certified (e.g., ISO 26262)
Example: How BSW Handles CAN Communication
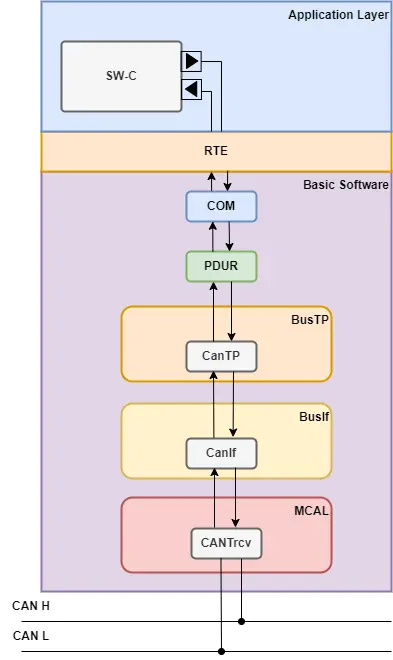
- Application calls a service to send data over CAN.
- RTE forwards this request to the COM stack (BSW Communication Service ) – Which is part of service layer.
- The COM stack processes the data and hands it to the PDU Router – Which is part of service layer.
- The PDU Router sends it to the CAN Interface (CanIf) – Which is part of ECU Abstraction layer, which further routes it to the CAN Driver (Which is part of MCAL).
- The driver transmits the data via the microcontroller’s CAN controller.
Tools Supporting BSW Development
Popular AUTOSAR-compliant toolchains used to configure and generate BSW:
- Vector DaVinci Developer
- ETAS ISOLAR
- Elektrobit Tresos
- Mentor Capital
- Artop Tool Platform (Eclipse-based)
These tools assist in configuring BSW modules through ARXML files, generating C code, and integrating with MCAL.
Conclusion
Basic Software (BSW) is the invisible but essential backbone of any AUTOSAR-based ECU. It provides the standard services and drivers that enable safe, reliable, and scalable automotive software development. Understanding BSW is crucial for embedded developers aiming to build software for tomorrow’s smart vehicles.

Leave a Reply