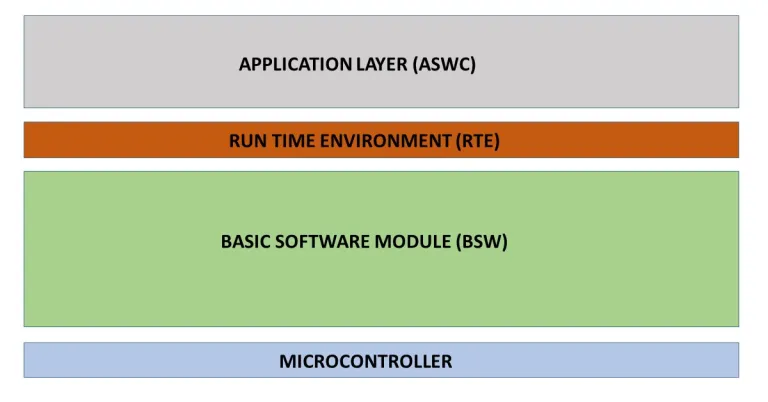
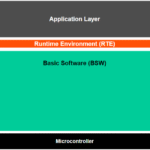
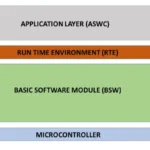
The Application Layer in AUTOSAR is where the actual automotive features are implemented — it’s the topmost layer in the AUTOSAR architecture and closest to the vehicle’s intended behavior (e.g., engine control, ADAS, lighting system, etc.).
1. What Is the Application Layer?
The Application Layer contains Application Software Components (SWCs) that define the vehicle’s functionality. Each component is independent, hardware-agnostic, and interacts with others via ports using the Run-Time Environment (RTE). For example:
- A Brake Control SWC
- A Rain Sensor SWC
- A Speed Monitor SWC
These are reusable, modular blocks developed using AUTOSAR rules.
2. Structure of the Application Layer
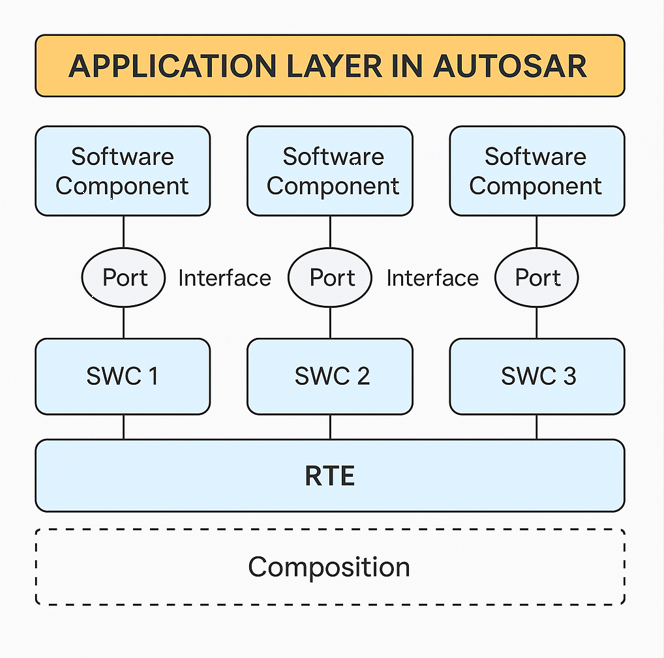
The application layer consists of:
🔹 Software Components (SWCs)
- Core units implementing logic (e.g., sensor reading, control algorithms).
- Communicate via ports and interfaces (sender-receiver, client-server).
- Independent of hardware thanks to AUTOSAR architecture.
🔹 Ports and Interfaces
- Ports: Entry/exit points for data and service communication.
- Interfaces: Define the type of communication (Sender/Receiver, Client/Server).
🔹 Compositions
- A logical grouping of SWCs that work together to provide higher-level functionality.
3. How It Works
- SWCs are modeled using tools (e.g., DaVinci Developer, EB tresos Studio).
- RTE is generated automatically to handle communication between SWCs and BSW.
- Application developers focus only on logic, not hardware or communication layers.
4. Example Use Case
Let’s say your car has automatic headlights. You can have:
LightSensorSWC– reads light intensity.HeadlightControlSWC– turns lights ON/OFF.- These SWCs communicate via RTE.
- No SWC cares about which microcontroller is used — AUTOSAR handles abstraction.
5. Benefits of AUTOSAR Application Layer
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reusability | SWCs can be reused across vehicle platforms |
| Modularity | Each function is encapsulated in its own SWC |
| Hardware Independence | Same logic can run on different hardware |
| Isolation & Safety | Failures in one SWC don’t break the whole system |
| Interoperability | Standardized communication between components |
Summary
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| SWC | Application logic unit |
| Port | Connection point for communication |
| Interface | Defines communication type |
| RTE | Middleware enabling SWC communication |
| Composition | Logical grouping of SWCs |

Leave a Reply