In the AUTOSAR (AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture) standard, the Runtime Environment (RTE) is one of the most critical components. It acts as a bridge between the application software and the Basic Software (BSW), ensuring that software components (SWCs) can communicate seamlessly with each other and with the underlying system.
What Is the RTE?
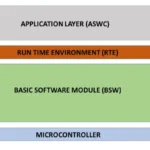
The RTE (Runtime Environment) is a middleware layer in the AUTOSAR architecture that provides an abstraction between the application layer and the basic software. It ensures that AUTOSAR Software Components (SWCs) can run independently of the microcontroller and the operating system used in the vehicle. Think of RTE as the “middleware translator” — it connects, routes, and manages data exchanged between software components and hardware-related services.
Why is RTE Important?
- Modularity
RTE allows developers to build reusable, independent software components without worrying about hardware dependencies. - Interoperability
It standardizes how components communicate, which is crucial when multiple suppliers contribute to the same ECU. - Scalability
Whether it’s a small microcontroller-based system or a high-performance controller, RTE enables scalability of the software across different ECUs. - Ease of Integration
Since RTE automatically generates code that connects SWCs with BSW modules, developers save time during integration.
Key Responsibilities of RTE
- Communication Between SWCs
RTE routes messages and service calls between components using ports and interfaces defined in the application layer. - Interaction with BSW Services
Through standardized APIs, RTE connects applications with services like NVRAM management, communication stacks, diagnostics, and OS services. - Data Handling
It manages data types, data transformation, buffering, and timing to meet the requirements of each signal or service. - Event and Trigger Management
RTE ensures that operations are triggered by the correct events, such as time intervals, data reception, or service requests.
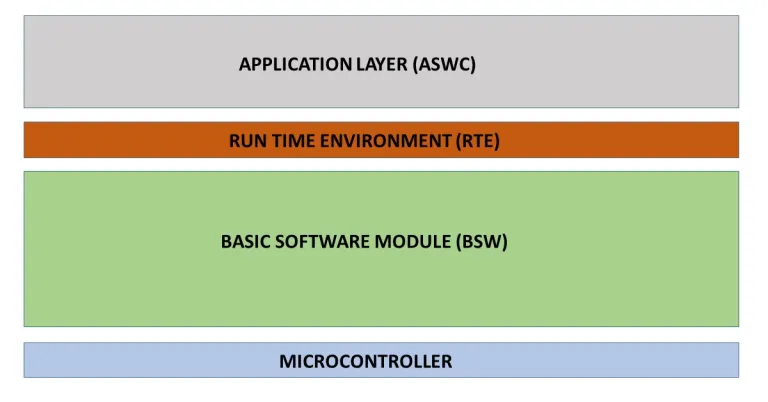
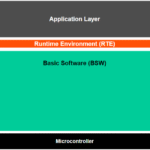
Where is RTE Located in the AUTOSAR Architecture?
In the layered AUTOSAR architecture:
[ Application Layer ]
↑
[ RTE ] ← Middleware Layer
↓
[ Basic Software Layer (BSW) ]
- Above RTE: You’ll find Software Components (SWCs) communicating via provided/required ports.
- Below RTE: The Basic Software (BSW), such as ECU Abstraction, Services, and Microcontroller Abstraction Layer (MCAL).
How is RTE Generated?
RTE is not handwritten — it’s generated automatically using AUTOSAR authoring tools (e.g., Vector DaVinci Developer, Elektrobit Tresos Studio, or ETAS ISOLAR-A). These tools use:
- The System Description (ARXML) file
- Component and ECU configuration files
Once the configuration is completed, the toolchain generates RTE source code (e.g., .c/.h files), which is then compiled along with the rest of the application.
Real-World Use Case Example
Imagine a Brake Control ECU where:
- One SWC reads brake pedal input.
- Another SWC calculates braking force.
- A third SWC sends commands to the actuator.
The RTE manages the communication between these components — transferring data, triggering operations, and ensuring timing constraints are met — all without developers having to write the low-level glue code.
Summary
| Feature | Role in RTE |
|---|---|
| Communication | Routes data and operations between SWCs and BSW |
| Abstraction | Hides hardware and OS details from application |
| Code Generation | Automatically generated from system configuration |
| Modularity | Enables reusable, hardware-independent software |
Final Thoughts
The RTE layer is what brings AUTOSAR’s promise of modularity, scalability, and standardization to life. As an embedded developer in automotive, understanding how RTE works — and how it fits into the big picture — is essential for working effectively within AUTOSAR projects.

Leave a Reply